Ácido flavogallonico
Apariencia
| Ácido flavogallonico | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| General | ||
| Fórmula estructural |
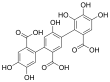 | |
| Fórmula molecular | C21H14O12 | |
| Identificadores | ||
|
OC(=O)c1cc(O)c(O)c(O)c1-c2cc(C(=O)O)c(cc2O)-c(cc3O)c(C(=O)O)cc3O
| ||
| Propiedades físicas | ||
| Masa molar | 458,32 g/mol | |
| Valores en el SI y en condiciones estándar (25 ℃ y 1 atm), salvo que se indique lo contrario. | ||
Ácido flavogallonico es un tanino hidrolizable que se puede encontrar en Quercus macrolepis[1] en los castaños[2] o en Terminalia myriocarpa.[3]
Referencias[editar]
- ↑ Molecular investigation of valonea tannin. Hasan Özgunay and Özcan Sari, The Journal of the American Leather Chemists Association, 2007, vol. 102, no5, pp. 154-157, INIST|18744048, text
- ↑ Considerations on the macromolecular structure of chestnut ellagitannins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Pasch H and Pizzi A, Journal of applied polymer science, 2002, vol. 85, no2, pp. 429-437, INIST|14185517
- ↑ Pharmacologically Active Ellagitannins from Terminalia myriocarpa. Mohamed S.A. Marzouk, Sayed A.A. El-Toumy, Fatma A. Moharram, Nagwa M.M. Shalaby and Amany A.E. Ahmed, Planta Med, 2002, 68(6), pages 523-527, doi 10.1055/s-2002-32549
Enlaces externos[editar]
- Esta obra contiene una traducción derivada de «Flavogallonic acid» de Wikipedia en inglés, publicada por sus editores bajo la Licencia de documentación libre de GNU y la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional.
