Núcleo reuniens
| Núcleo reuniens | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Latín | Nucleus reuniens | |
| TA | A14.1.08.632 | |
| Enlaces externos | ||
| NeuroLex ID | Reuniens nucleus | |
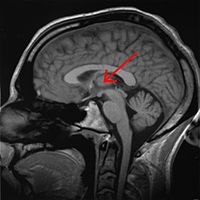
El núcleo reuniens es un componente del grupo nuclear medio del tálamo. En los mamíferos, está situado en la adhesión intertalámica (masa intermedia del tálamo).[1]

Conexiones
[editar]
El núcleo reuniens recibe aferencias desde un gran número de estructuras, principalmente del sistema límbico y de estructuras asociadas a él.[2]
Por otra parte, envía proyecciones al córtex prefrontal medial, al hipocampo, y a la corteza entorrinal; aunque también existen escasas conexiones eferentes con el sistema límbico.[3][4][5] Las conexiones frontohipocampales le permiten regular una gran cantidad de información relacionada con la atención, así como contribuir al aprendizaje asociativo, la planificación de una ruta espacial, y la generalización de la memoria.[6][7][8][9]
Referencias
[editar]- ↑ Carpenter, Malcolm; Sutin, Jerome (1983). Human Neuroanatomy. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins. pp. 504–510. ISBN 0-683-01461-7.
- ↑ McKenna, J. T.; Vertes, R. P. (2004). «Afferent projections to nucleus reuniens of the thalamus». The Journal of Comparative Neurology 480 (2): 115-142. PMID 15514932. doi:10.1002/cne.20342.
- ↑ Wouterlood, F. G.; Saldana, E.; Witter, M. P. (1990). «Projection from the nucleus reuniens thalami to the hippocampal region: Light and electron microscopic tracing study in the rat with the anterograde tracerPhaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin». The Journal of Comparative Neurology 296 (2): 179-203. PMID 2358531. doi:10.1002/cne.902960202.
- ↑ Vertes, R. P. (2006). «Interactions among the medial prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and midline thalamus in emotional and cognitive processing in the rat». Neuroscience 142 (1): 1-20. PMID 16887277. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.06.027.
- ↑ Herkenham, M. (1978). «The connections of the nucleus reuniens thalami: Evidence for a direct thalamo-hippocampal pathway in the rat». The Journal of Comparative Neurology 177 (4): 589-610. PMID 624792. doi:10.1002/cne.901770405.
- ↑ Vertes, R. P.; Hoover, W. B.; Szigeti-Buck, K.; Leranth, C. (2007). «Nucleus reuniens of the midline thalamus: Link between the medial prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus». Brain Research Bulletin 71 (6): 601-609. PMID 17292803. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.12.002.
- ↑ Eleore, L.; López-Ramos, J. C.; Guerra-Narbona, R.; Delgado-García, J. M. (2011). «Role of Reuniens Nucleus Projections to the Medial Prefrontal Cortex and to the Hippocampal Pyramidal CA1 Area in Associative Learning». En Izquierdo, Ivan, ed. PLoS ONE 6 (8): e23538. PMC 3156136. PMID 21858159. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023538.
- ↑ Ito, H. T.; Zhang, S. J.; Witter, M. P.; Moser, E. I.; Moser, M. B. (2015). «A prefrontal-thalamo-hippocampal circuit for goal-directed spatial navigation». Nature 522 (7554): 50-5. PMID 26017312. doi:10.1038/nature14396.
- ↑ Xu, W.; Sudhof, T. C. (14 de marzo de 2013). «A Neural Circuit for Memory Specificity and Generalization». Science 339 (6125): 1290-1295. PMID 23493706. doi:10.1126/science.1229534.
