Diferencia entre revisiones de «5-metoxitriptamina»
Apariencia
Contenido eliminado Contenido añadido
Creado al traducir la página «5-Methoxytryptamine» |
Creado al traducir la página «5-Methoxytryptamine» |
||
| Línea 33: | Línea 33: | ||
La '''5-metoxitriptamina''' (abreviado '''5-MT'''), también conocida como '''mexamina''', es un [[Derivado (química)|derivado]] de la [[triptamina]] estrechamente relacionado con los [[Neurotransmisor|neurotransmisores]] [[serotonina]] y [[melatonina]]. Se ha demostrado que la 5-MT se produce naturalmente en animales en bajos niveles.<ref name="pmid2460575">{{Cita publicación|título=Day-night rhythm of 5-methoxytryptamine biosynthesis in the pineal gland of the golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus).|apellidos=Galzin AM, Eon MT, Esnaud H, Lee CR, Pévet P, Langer SZ|publicación=J. Endocrinol.|volumen=118|número=3|páginas=389–397|doi=10.1677/joe.0.1180389|pmid=2460575|año=1988}}</ref> Se biosintetiza a través de la [[Acetilación|deacetilación]] de la melatonina en la [[glándula pineal]].<ref name="pmid2460575" /> |
La '''5-metoxitriptamina''' (abreviado '''5-MT'''), también conocida como '''mexamina''', es un [[Derivado (química)|derivado]] de la [[triptamina]] estrechamente relacionado con los [[Neurotransmisor|neurotransmisores]] [[serotonina]] y [[melatonina]]. Se ha demostrado que la 5-MT se produce naturalmente en animales en bajos niveles.<ref name="pmid2460575">{{Cita publicación|título=Day-night rhythm of 5-methoxytryptamine biosynthesis in the pineal gland of the golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus).|apellidos=Galzin AM, Eon MT, Esnaud H, Lee CR, Pévet P, Langer SZ|publicación=J. Endocrinol.|volumen=118|número=3|páginas=389–397|doi=10.1677/joe.0.1180389|pmid=2460575|año=1988}}</ref> Se biosintetiza a través de la [[Acetilación|deacetilación]] de la melatonina en la [[glándula pineal]].<ref name="pmid2460575" /> |
||
La 5-MT actúa como un [[Agonista|agonista total]] en los receptores [[Receptor 5-HT1|5-HT<sub>1</sub>]], [[Receptor 5-HT2|5-HT<sub>2</sub>]], [[Receptor 5-HT4|5-HT<sub>4</sub>]], [[Receptor 5-HT6|5-HT<sub>6</sub>]] y [[Receptor 5-HT7|5-HT<sub>7</sub>]].<ref name="pmid2966313">{{Cita publicación|título=Serotonin-1A receptor activation in hippocampal CA1 neurons by 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin, 5-methoxytryptamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine.|apellidos=Wu PH, Gurevich N, Carlen PL|publicación=Neurosci. Lett.|volumen=86|número=1|páginas=72–76|doi=10.1016/0304-3940(88)90185-1|pmid=2966313|año=1988}}</ref><ref name="pmid9128844">{{Cita publicación|título=Hyperglycemia induced by the 5-HT receptor agonist, 5-methoxytryptamine, in rats: involvement of the peripheral 5-HT2A receptor.|apellidos=Yamada J, Sugimoto Y, Yoshikawa T, Horisaka K|publicación=Eur J Pharmacol|volumen=323|número=2–3|páginas=235–240|doi=10.1016/S0014-2999(97)00029-0|pmid=9128844|año=1997}}</ref><ref name="pmid9016931">{{Cita publicación|título=Characterization of the contractile response induced by 5-methoxytryptamine in rat stomach fundus strips.|apellidos=Amemiya N, Hatta S, Takemura H, Ohshika H|publicación=Eur J Pharmacol|volumen=318|número=2–3|páginas=403–409|doi=10.1016/S0014-2999(96)00777-7|pmid=9016931|año=1996}}</ref><ref name="pmid2402303">{{Cita publicación|título=5-Methoxytryptamine and 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine-induced desensitization as a discriminative tool for the 5-HT3 and putative 5-HT4 receptors in guinea pig ileum.|apellidos=Craig DA, Eglen RM, Walsh LK, Perkins LA, Whiting RL, Clarke DE|publicación=Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol|volumen=342|número=1|páginas=9–16|doi=10.1007/bf00178965|pmid=2402303|año=1990}}</ref><ref name="pmid9225298">{{Cita publicación|título=Functional and radioligand binding characterization of rat 5-HT6 receptors stably expressed in HEK293 cells.|apellidos=Boess FG, Monsma Jr FJ, Carolo C, Meyer V, Rudler A, Zwingelstein C, Sleight AJ|publicación=Neuropharmacology|volumen=36|número=4–5|páginas=713–720|doi=10.1016/S0028-3908(97)00019-1|pmid=9225298|año=1997}}</ref><ref name="pmid10051134">{{Cita publicación|título=[3H]-Mesulergine labels 5-HT7 sites in rat brain and guinea-pig ileum but not rat jejunum.|apellidos=Hemedah M, Coupar IM, Mitchelson FJ|publicación=Br J Pharmacol|volumen=126|número=1|páginas=179–188|doi=10.1038/sj.bjp.0702293|pmc=1565797|pmid=10051134|año=1999}}</ref><ref name="urlSerotonin Receptor Subtypes and Ligands">{{Cita web|url=http://www.acnp.org/g4/GN401000039/Ch039.html|título=Serotonin Receptor Subtypes and Ligands|fechaacceso=2008-04-11|fecha=2000-01-01|editorial=American College of Neurophyscopharmacology|urlarchivo=https://web.archive.org/web/20080421160353/http://www.acnp.org/g4/GN401000039/Ch039.html|fechaarchivo=21 April 2008|url-status=live}}</ref> No tiene afinidad por el receptor [[Receptor 5-HT3|5-HT<sub>3</sub>]] y su afinidad por el receptor 5-HT<nowiki><sub id="mwMQ">1E</sub></nowiki> es muy débil en comparación con los otros receptores 5-HT<sub>1</sub> . <ref name="pmid2402303" /> <ref name="bookThe Serotonin Receptors">{{Cita libro|título=The serotonin receptors|apellidos=Roth|nombre=Brian|año=2006|editorial=Humana Press|isbn=978-1-58829-568-2|página=133}}</ref> Se desconoce su afinidad por el [[Receptor 5-HT5|receptor 5-HT<sub>5</sub>]]. |
|||
Afinidad medida para el caso de algunos receptores: |
|||
* Receptores 5-HT <nowiki><sub id="mwQg">1B</sub></nowiki> (K <sub>i</sub> = 35 nM) <ref name="Domenech">S. Nigra / Domenech T, et al., 1997</ref> |
|||
* Receptores [[Receptor 5-HT1D|5-HT <sub>1D</sub>]] (K <sub>i</sub> = 7,3 nM) <ref name="PEROUTKA">Cortex / PEROUTKA ET AL., 1989</ref> |
|||
* Receptores 5-HT <nowiki><sub id="mwTg">1E</sub></nowiki> ( <sub>Ki</sub> = 3151 nM) <ref name="ZGOMBICK">Cloned / ZGOMBICK JM, ET AL., 1992</ref> |
|||
* Receptores 5-HT <nowiki><sub id="mwVA">1F</sub></nowiki> ( <sub>Ki</sub> = 1166 nM) <ref name="Adham">Cloned / Adham N, et al., 1992</ref> |
|||
* Receptores [[Receptor 5-HT2A|5-HT <sub>2A</sub>]] (K <sub>i</sub> = 295 nM) <ref name="HOYER">Cortex / HOYER ET AL., 1987</ref> |
|||
* Receptores 5-HT <nowiki><sub id="mwYA">2B</sub></nowiki> (K <sub>i</sub> = 16,4 nM) <ref name="WAINSCOTT">Cortex / WAINSCOTT DB, ET AL., 1996</ref> |
|||
* Receptores 5-HT <nowiki><sub id="mwZg">2C</sub></nowiki> (K <sub>i</sub> = 52,48 nM) <ref name="BONHAUS">Cloned / BONHAUS DW, ET AL., 1997</ref> |
|||
* Receptores [[Receptor 5-HT4|5-HT <sub>4</sub>]] (K <sub>i</sub> = 501,18 nM) <ref name="ANSANAY">Caudate / ANSANAY H, ET AL.,1996</ref> |
|||
* Receptores [[Receptor 5-HT6|5-HT <sub>6</sub>]] (K <sub>i</sub> = 69,18 nM) <ref name="Hirst">Cloned / Hirst WD, et.al.,2003</ref> |
|||
* Receptores [[Receptor 5-HT7|5-HT <sub>7</sub>]] ( <sub>Ki</sub> = 5,01 nM) <ref name="BOESS">Cloned / BOESS FG, ET AL., 1994</ref> |
|||
== Véase también == |
|||
* 2-metil-5-hidroxitriptamina |
|||
* 5-benciloxitriptamina |
|||
* 5-carboxamidotriptamina |
|||
* α-metil-5-hidroxitriptamina |
|||
== Referencias == |
|||
{{Listaref|30em}} |
|||
[[Categoría:Serotonina]] |
|||
Revisión del 23:22 1 may 2023
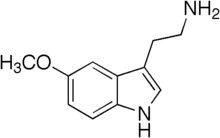
| 5-metoxitriptamina | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Identificadores | ||
| Número CAS | 608-07-1 | |
| PubChem | 1833 | |
| ChemSpider | 1767 | |
| UNII | 3VMW6141KC | |
| KEGG | C05659 | |
| ChEBI | 2089 | |
| ChEMBL | 8165 | |
| Datos químicos | ||
| Fórmula | C11H14N2O | |
|
InChI=1S/C11H14N2O/c1-14-9-2-3-11-10(6-9)8(4-5-12)7-13-11/h2-3,6-7,13H,4-5,12H2,1H3
Key: JTEJPPKMYBDEMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
La 5-metoxitriptamina (abreviado 5-MT), también conocida como mexamina, es un derivado de la triptamina estrechamente relacionado con los neurotransmisores serotonina y melatonina. Se ha demostrado que la 5-MT se produce naturalmente en animales en bajos niveles.[1] Se biosintetiza a través de la deacetilación de la melatonina en la glándula pineal.[1]
La 5-MT actúa como un agonista total en los receptores 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT4, 5-HT6 y 5-HT7.[2][3][4][5][6][7][8] No tiene afinidad por el receptor 5-HT3 y su afinidad por el receptor 5-HT<sub id="mwMQ">1E</sub> es muy débil en comparación con los otros receptores 5-HT1 . [5] [9] Se desconoce su afinidad por el receptor 5-HT5.
Afinidad medida para el caso de algunos receptores:
- Receptores 5-HT <sub id="mwQg">1B</sub> (K i = 35 nM) [10]
- Receptores 5-HT 1D (K i = 7,3 nM) [11]
- Receptores 5-HT <sub id="mwTg">1E</sub> ( Ki = 3151 nM) [12]
- Receptores 5-HT <sub id="mwVA">1F</sub> ( Ki = 1166 nM) [13]
- Receptores 5-HT 2A (K i = 295 nM) [14]
- Receptores 5-HT <sub id="mwYA">2B</sub> (K i = 16,4 nM) [15]
- Receptores 5-HT <sub id="mwZg">2C</sub> (K i = 52,48 nM) [16]
- Receptores 5-HT 4 (K i = 501,18 nM) [17]
- Receptores 5-HT 6 (K i = 69,18 nM) [18]
- Receptores 5-HT 7 ( Ki = 5,01 nM) [19]
Véase también
- 2-metil-5-hidroxitriptamina
- 5-benciloxitriptamina
- 5-carboxamidotriptamina
- α-metil-5-hidroxitriptamina
Referencias
- ↑ a b Galzin AM, Eon MT, Esnaud H, Lee CR, Pévet P, Langer SZ (1988). «Day-night rhythm of 5-methoxytryptamine biosynthesis in the pineal gland of the golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus).». J. Endocrinol. 118 (3): 389-397. PMID 2460575. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1180389.
- ↑ Wu PH, Gurevich N, Carlen PL (1988). «Serotonin-1A receptor activation in hippocampal CA1 neurons by 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin, 5-methoxytryptamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine.». Neurosci. Lett. 86 (1): 72-76. PMID 2966313. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(88)90185-1.
- ↑ Yamada J, Sugimoto Y, Yoshikawa T, Horisaka K (1997). «Hyperglycemia induced by the 5-HT receptor agonist, 5-methoxytryptamine, in rats: involvement of the peripheral 5-HT2A receptor.». Eur J Pharmacol 323 (2–3): 235-240. PMID 9128844. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(97)00029-0.
- ↑ Amemiya N, Hatta S, Takemura H, Ohshika H (1996). «Characterization of the contractile response induced by 5-methoxytryptamine in rat stomach fundus strips.». Eur J Pharmacol 318 (2–3): 403-409. PMID 9016931. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(96)00777-7.
- ↑ a b Craig DA, Eglen RM, Walsh LK, Perkins LA, Whiting RL, Clarke DE (1990). «5-Methoxytryptamine and 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine-induced desensitization as a discriminative tool for the 5-HT3 and putative 5-HT4 receptors in guinea pig ileum.». Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 342 (1): 9-16. PMID 2402303. doi:10.1007/bf00178965.
- ↑ Boess FG, Monsma Jr FJ, Carolo C, Meyer V, Rudler A, Zwingelstein C, Sleight AJ (1997). «Functional and radioligand binding characterization of rat 5-HT6 receptors stably expressed in HEK293 cells.». Neuropharmacology 36 (4–5): 713-720. PMID 9225298. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(97)00019-1.
- ↑ Hemedah M, Coupar IM, Mitchelson FJ (1999). «[3H]-Mesulergine labels 5-HT7 sites in rat brain and guinea-pig ileum but not rat jejunum.». Br J Pharmacol 126 (1): 179-188. PMC 1565797. PMID 10051134. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0702293.
- ↑ «Serotonin Receptor Subtypes and Ligands». American College of Neurophyscopharmacology. 1 de enero de 2000. Archivado desde el original el 21 April 2008. Consultado el 11 de abril de 2008. Parámetro desconocido
|url-status=ignorado (ayuda) - ↑ Roth, Brian (2006). The serotonin receptors. Humana Press. p. 133. ISBN 978-1-58829-568-2.
- ↑ S. Nigra / Domenech T, et al., 1997
- ↑ Cortex / PEROUTKA ET AL., 1989
- ↑ Cloned / ZGOMBICK JM, ET AL., 1992
- ↑ Cloned / Adham N, et al., 1992
- ↑ Cortex / HOYER ET AL., 1987
- ↑ Cortex / WAINSCOTT DB, ET AL., 1996
- ↑ Cloned / BONHAUS DW, ET AL., 1997
- ↑ Caudate / ANSANAY H, ET AL.,1996
- ↑ Cloned / Hirst WD, et.al.,2003
- ↑ Cloned / BOESS FG, ET AL., 1994
