Usuario:Danna Iveth
COAL

Coal is a sedimentary rock of organic origin, black or dark brown. It is used mainly as a fossil fuel for its heating capacity because it has a majority carbon content. Coals can be classified by the percentage of carbon they contain, which is related to the percentage of moisture and impurities. According to this criterion, peat, lignite, coal and anthracite can be distinguished.
Composition of coal
The coal element appears in coal in a percentage higher than 50% by weight and 70% by volume. The water that it contains (humidity) is variable and comes from the one that was trapped at the time of coal formation.
Other components of coal are mineral matter (various silicates) and carbonate minerals (siderite, calcite and aragonite). Pyrite is a mineral with sulfur very common in coals. There are small amounts of metals, such as iron, uranium, cadmium and, in very small quantities, gold.
Methane is a gas found in coal mines and can be the source of dangerous explosions in underground mines. In this specific context you will be & rsquo; usually called gray.
Origin of coal
It is believed that most of the real coal was formed during the Carboniferous period (280 to 345 million years ago) of the Primary Era. Also in the Permian, Triassic and Jurassic large deposits were formed. In the Cretaceous, lignite was formed. There is currently peat formation in the peat bogs.
Coal from Europe, Asia and North America is formed mainly in the coal-based tropical vegetation.
Southern hemisphere coal was formed with cold climate vegetation (tundra). The old plants through the geological changes have comparisons, hardened, chemically altered and undergoing a process of metamorphosis by temperature and pressure.
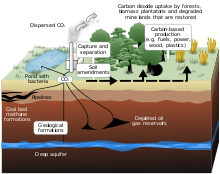
Coal from the northern hemisphere was formed in wetland ecosystems called carboniferous forests. When plants die and accumulate in aquatic environments with little oxygen (anaerobic media), they undergo bacterial degradation. For the formation of coal it is necessary that these conditions have a time duration, and without erosion in sedimentary conditions.
History of the use of coal
The British Isles (especially rich in coal and where the industrial revolution began) are the first place studied where the use of this fossil fuel is detected.
There, in the third millennium BC, it was found to be a component of funeral pyres and by 200 BC there is evidence, in the same area, of commercial activity and of being used to dry cereals. Under Roman domination there are mentions of the sporadic use of coal, but until the Middle Ages.
The first coal used was simply collected from the beach, when this source was exhausted it had to go to coal mining. It began to be used massively with the first applications of the steam engine, both in industry and transport, especially in trains and ships.
In the 20th century, when coal became quite expensive, liquid fossil fuels (petroleum derivatives) began to be preferred for transport, and from the middle of the century the use
of natural gas was increasing in favor of oil and gas. coal in industry and obtaining energy. However, even in the 21st century coal is used to obtain & rsquo; thermal energy (heat) and electricity in industrial boilers and thermal power plants.
Currently, the main problems are pollution and sustainability, as it is a natural resource in the process of depletion.
Use of coal
Coal is used mainly as a primary source of heat in industrial boilers and for obtaining electricity in the coal combustion chambers (fixed bed or fluid bed) of the thermoelectric plants. It is, then, mainly a fuel, which can be classified within fossil fuels. 75% of the world's coal is used to produce electricity. The global energy efficiency of coal plants is not very high, around 25% -27%.
It also has other lesser uses, among which are, for example, cement kilns and the production of coking coal from coal to produce steel.
Two technologies with great prospects for the future are gasification and coal liquefaction. The first is older, it was already used in the eighteenth century to obtain what was then called water gas and currently has the interest of producing gaseous fuel synthetic fingers (synthetic natural gas or GNS, hydrogen, etc.), which pretend be easier to store and transport, in addition to being more environmentally friendly, than solid charcoal. Coal liquefaction began in Germany during the Second World War, so as not to depend on the other countries for oil and its derivatives, since they had no oil deposits but coal mines. As the oil runs out in the world, this technique, direct or indirect, is becoming more advantageous every day, and also allows producing less polluting fuels and designed to be more suitable for use in the automotive industry. The liquid fuel obtained by the liquefaction of coal has twice the calorific power of the coal used to make it.
Time line on carbon
- It was discovered in prehistory and was already known in antiquity in which it was manufactured by incomplete combustion of organic materials.
- Newton, in 1704, intuited that the diamond could be fuel.
- it was not possible to burn a diamond until 1772 when Lavoisier showed that CO2 was produced in the combustion reaction.
- Tennant showed that the diamond was pure carbon in 1797.
- The first carbon compounds were identified in living matter at the beginning of the 19th century, and for this reason the study of carbon compounds was called organic chemistry.
- 1852-1911 Jacobus henricus van't hoff proposed the tetrahedral orientation of the valences in the atom of carbon that gives birth to the stereochemistry.
- 1857-1858 Kekule was the main driver of the theory of chemical structure.
- 1858 Broad concept to include the idea of coal can be linked in chains.
- 1860 Start the first international congress of chemists where I treat subjects on the nomenclature and definitions of the atom, molecule and equivalence.
- 1862 August kekule, I publish the theory of compounds saturated with carbón.
- 1865 Kekule published an article in which he suggested that the structure contains a ring of six-membered carbon atoms with alternating single and double bonds.
- 1872 Thanks to his contributions he contributes in the synthesis of the aromatic compounds.
- 1957 I publish a document in which the diary of annalen der chemier on the tetravelence of coal.
- The last known allotropes, the fullerenes (C60), were discovered as a by-product in experiments carried out with molecular gases in the 1980s.
- The radioactive isotope carbon-14, discovered on February 27, 1940, is used in radiometric dating.
- The most common isotope of carbon is 12C; in 1961 this isotope was chosen to replace the oxygen-16 isotope as the basis for atomic weights, and was assigned an atomic weight of 12.
